Find which tap in your marketing strategy is not working with attribution modeling and channelize them to work more effectively
Practicing different methods and approaches while running campaigns is a vital part of marketing, but to keep an eye on whether these methods are working or not, attribution modeling comes into sight.
Attribution modeling in market research plays a vital role in understanding the contribution of various marketing channels and touchpoints towards achieving marketing goals. By identifying the key components of attribution modeling, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behavior, optimize marketing strategies, and allocate resources more effectively. In further reading, we will explore the essential components of attribution modeling, including first-click attribution, last-click attribution, time decay attribution, U-shaped attribution, and W-shaped attribution.
Data Collection and Integration
The first step in attribution modeling is collecting and integrating data from multiple sources, including website analytics, advertising platforms, CRM systems, and more. This comprehensive data collection enables marketers to have a holistic view of customer interactions across different channels and touchpoints.
Attribution Models
Credit for a customer’s eventual purchase can be distributed across various marketing channels and touchpoints using attribution models. Let’s explore six common attribution models:
a. First-Click Attribution
This model assigns all the credit for a conversion to the first touchpoint or marketing channel that the customer interacted with. It emphasizes the initial engagement that captured the customer’s attention and triggered their interest. First-click attribution is beneficial for understanding the channels that drive awareness and introduce customers to a brand.
b. Last-Click Attribution
In contrast to first-click attribution, the last-click attribution model assigns all the credit for a conversion to the last touchpoint or marketing channel that directly led to the conversion. It focuses on the final action that prompted the customer to make a purchase or complete a desired goal. Last-click attribution is useful for identifying the channels that have the strongest influence on conversions.
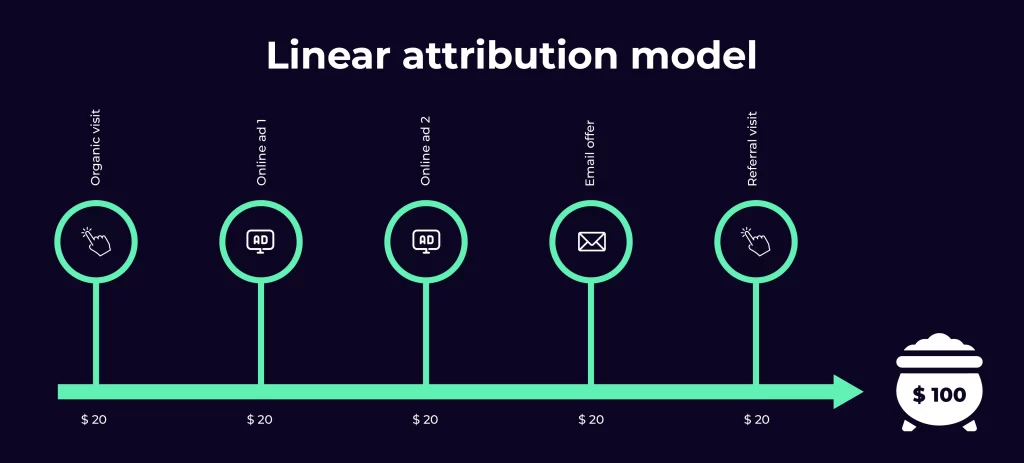
c. Linear Attribution
The linear attribution model assigns equal credit to all touchpoints throughout the customer journey. It acknowledges the contribution of each touchpoint without emphasizing any specific interaction. The linear model provides a fair distribution of credit across all touchpoints. Explained in infographic shown below:
d. Time Decay Attribution
This model assigns credit to all touchpoints along the customer journey, with more weight given to the touchpoints that are closer to the conversion. It recognizes that multiple interactions influence a customer’s decision and considers the recency of those interactions. Time decay attribution provides a balanced view of the entire customer journey and accounts for the cumulative impact of touchpoints over time.
e. U-Shaped Attribution
The U-shaped attribution model gives credit to the first touchpoint, the touchpoints in the middle of the customer journey, and the last touchpoint. It acknowledges that the first interaction creates awareness, the middle interactions nurture the customer’s interest, and the final interaction seals the deal. The U-shaped model is useful for giving proper credit to the key touchpoints that contribute to conversions.
f. W-Shaped Attribution
The W-shaped attribution model assigns credit to the first touchpoint, the touchpoints in the middle of the customer journey, and the last touchpoint, but with additional weight given to the touchpoints in the middle. This model recognizes that specific touchpoints in the middle of the customer journey have a significant impact on the customer’s decision-making process. The W-shaped model is beneficial for understanding the influential touchpoints that drive conversions.
Stat Insights
Currently 52% of marketers make use of attribution reporting. (Hubspot)
Over 36% of B2B business have adopted Persona & Customer journey Mapping (Statista)
Touchpoint Mapping
Understanding the customer journey and mapping out the touchpoints is a crucial component of attribution modeling. It involves identifying the various interactions a customer has with a brand, from the initial exposure to the final conversion. This process helps in visualizing the customer’s decision-making process and identifying the key touchpoints that contribute most significantly to conversions.
Cross-Channel Analysis
Attribution modeling requires analyzing the performance of marketing channels and campaigns across different channels, such as search, social media, email, display ads, and more. A proper comparison of effectiveness of these channels, businesses can identify the most influential and cost-efficient channels.
Machine Learning and Advanced Algorithms
To handle the complexity of attribution modeling and derive meaningful insights, machine learning and advanced algorithms play a significant role. These technologies enable marketers to process large volumes of data, identify patterns, and make accurate predictions. Neet usage of machine learning algorithms, businesses can uncover hidden relationships and optimize marketing efforts.
Experimentation and Testing
Attribution modeling requires continuous experimentation and testing to refine the models and improve accuracy. Conducting A/B tests and running controlled experiments, marketers can assess the impact of different marketing strategies and make data-driven decisions.
Conclusion
Attribution modeling has become an essential tool for companies to gauge the success of their marketing initiatives in today’s dynamic market. Businesses can gain insights into customer behavior and fine-tune their marketing strategies by implementing the core components of attribution modeling, such as data collection and integration, attribution models (such as first-click attribution, last-click attribution, time decay attribution, U-shaped attribution, and W-shaped attribution), touchpoint mapping, cross-channel analysis, machine learning, and experimentation.
In a highly competitive market, firms who continue to engage in attribution modeling will be better able to make strategic decisions, manage resources efficiently, and provide outstanding customer experiences. Connect with us now to rightly apply business growth practices!